By Karissa Cottier, PhD
Immune activation, and the resulting inflammation, is an important component of liver homeostasis. During infection or situations resulting in acute liver injury, immune activation allows the liver to clear any pathogens and resolve damage through regeneration. Sustained uncontrolled inflammation, however, is a driving component of numerous liver diseases. Non-parenchymal cells (NPCs) of the liver, including Kupffer cells, orchestrate these immune responses. Kupffer cells, the resident macrophages of the liver, are localized to the hepatic sinusoid, allowing them to perform a surveillance role; enabling the liver to respond to pathogens and damage. The plasticity of the Kupffer cells’ response allows them to precisely regulate inflammation through phenotypic changes, resulting in differential expression of pro- or anti- inflammatory mediators. This critical regulation of inflammatory response by Kupffer cells makes them an important component of in vitro models of liver disease, as well as in vitro screening models for drug toxicity arising from inflammation-induced down-regulation of drug metabolizing enzymes (DME) and/or drug transporters.

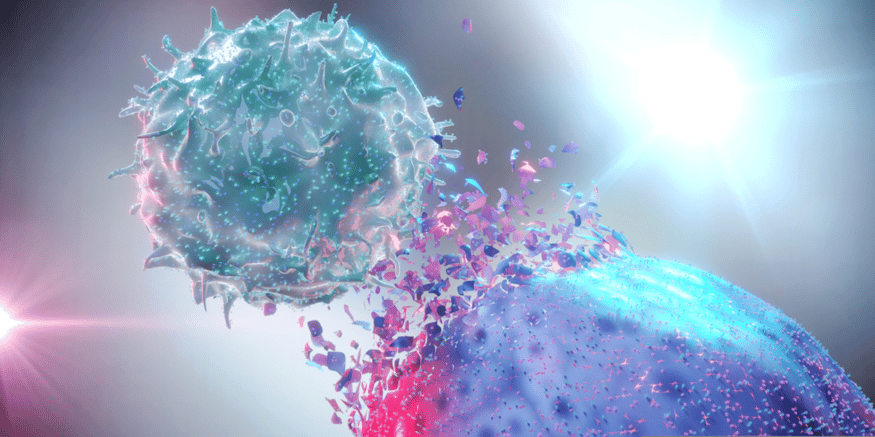



.png?width=875&name=Untitled%20design%20(40).png)
.png?width=875&name=Newsletter%20279%20x%20139%20(1).png)
.jpg?width=875&name=Kupffer%20Cell%2022JUN20%20(1).jpg)